Cloud migration & strategies
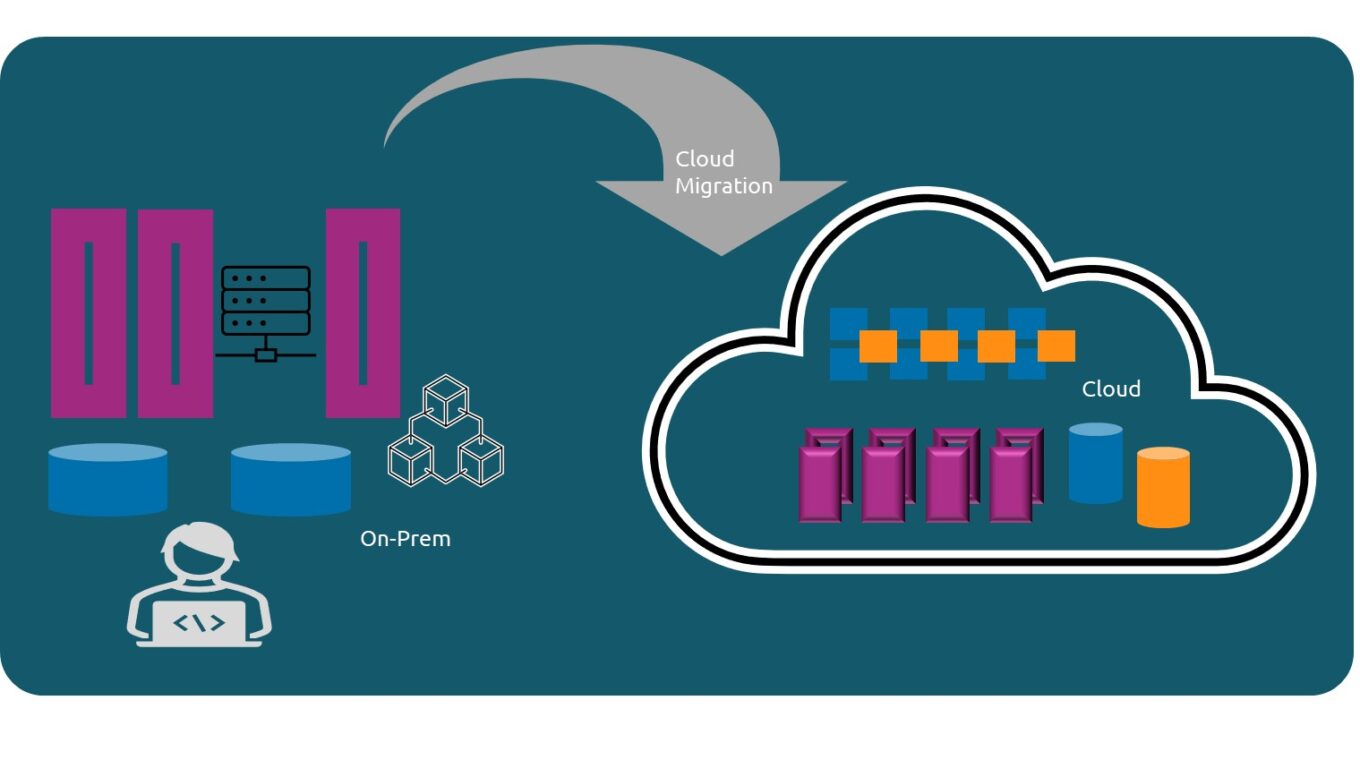
Cloud migration
Cloud migration refers to the process of moving data, applications, services, and other business elements from an organization’s on-premise infrastructure to a cloud computing environment. This migration involves transferring digital assets and operations to cloud-based platforms, which offer scalable resources, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional on-premise setups.
Cloud migration strategies
Cloud migration strategies encompass a range of approaches for transferring data, applications, and digital assets from on-premise environments to the cloud. Below are key cloud migration strategies from learnings…
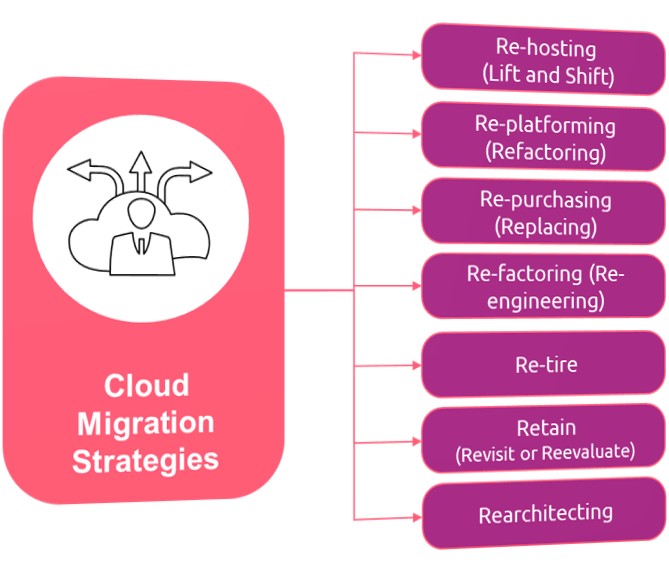
- Rehosting (Lift and Shift): Copying our existing setup to the cloud without major changes. It’s like moving our entire shop to a new location as-is.
Advantages:
Quick and straightforward migration
Minimal changes required
Disadvantages:
Limited cloud-native benefits
May not optimize costs or performance
- Replatforming (Refactoring): We making few adjustments to our applications to fit better in the cloud. It’s like renovating parts of our shop to make it more modern and efficient.
Advantages:
Improved performance and cost optimization
Aligns with cloud-native standards
Disadvantages:
Requires more time and effort for refactoring
Potential compatibility issues with existing systems
- Repurchasing (Replacing): Buying new cloud-based software instead of using our old on-premise systems. It’s like upgrading our appliances to newer, cloud-enabled versions.
Advantages
Access to new cloud-based features and services
Simplifies management and maintenance
Disadvantages
May involve additional costs for new subscriptions or licenses
Data migration challenges may arise
- Refactoring (Re-engineering): Restructuring our applications to take full advantage of cloud capabilities. It’s like rebuilding parts of our shop to make it smarter and more adaptable.
Advantages:
Leverages full potential of cloud-native capabilities
Enhanced scalability and agility
Disadvantages:
Requires significant development and testing efforts
Can be time-consuming and complex
- Retire: Getting rid of old applications or systems that we no longer need. It’s like decluttering our shop by removing items we don’t use anymore
Advantages:
Simplifies migration by reducing the scope
Eliminates obsolete or unnecessary systems
Disadvantages:
Potential data loss if not properly managed
Business processes may need to be adjusted
- Retain (Revisit or Re-evaluate): Keeping some things on-premise for now and reconsidering them for cloud migration later. It’s like deciding to keep some furniture in storage and deciding if we use it again in the future.
Advantages
Maintains compliance or data sovereignty requirements
Allows for future cloud migration consideration
Disadvantages
Limits access to cloud benefits and scalability
May delay overall digital transformation efforts
- Rearchitecting: Completely redesigning our applications to be fully cloud-native. It’s like designing a new shop from scratch to take advantage of the latest building technologies.
Advantages:
Fully optimizes applications for cloud-native environments
Enhanced scalability, resilience, and performance
Disadvantages:
Requires substantial redesign and development efforts
Higher upfront investment and technical expertise may be needed
In summary, Cloud migration is a strategic move for businesses, offering agility and cost-efficiency. Leveraging the right strategies is key to unlocking the cloud’s full potential for innovation and competitiveness

