Estimation in Agile way
There are various methods to estimate work items in Agile processes, the popularly used estimation techniques are t-shirt sizing, Poker Planning,..
whole team to gathers around a table to estimate the all the work items using relative comparisons; But today’s Agile teams are mostly distributed, so physical poker decks can be of limited use. If everyone on the team, including remote teams, has their own poker deck, you still can play with the remote members by showing their cards on camera. However, the fun of being there gets lost.
In practice, most companies have tackled this problem by using collaborative tools such as skype chat, all the team members will share the estimation during the estimation process using this tool to use with remote teams. Agile lead must facilitate this procedure to ensure all distributed agile team members engaged throughout.
Story point
It is a subjective unit of estimation used by Agile teams to estimate User Stories.
Story point generally allocated based on:
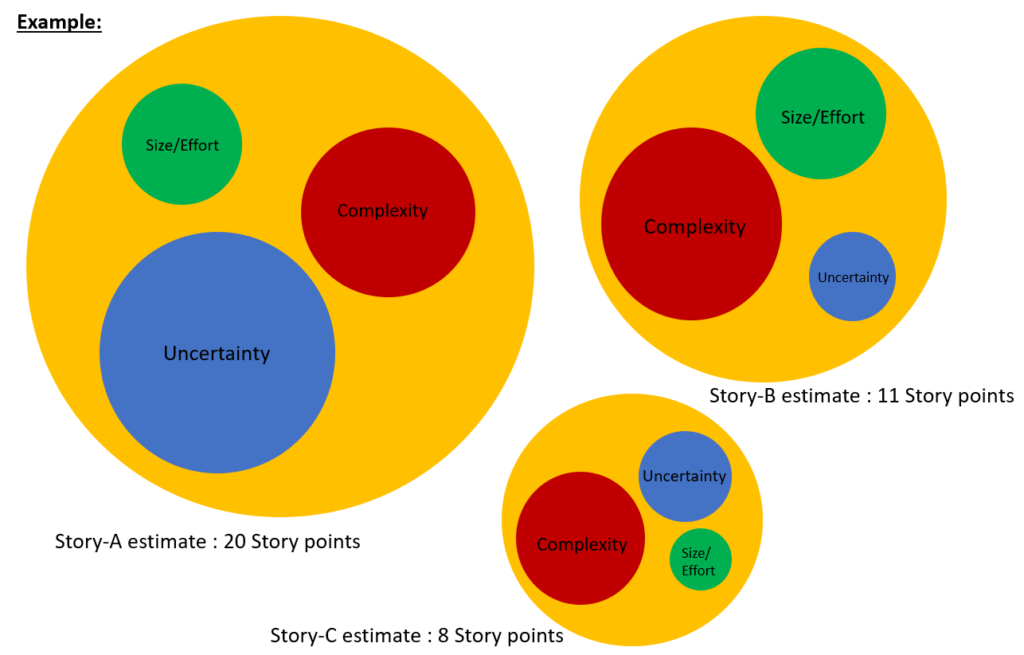
- How “hard” story to implement? ( Complexity )
- How “much” the story is? ( Size )
- How much is unknown ! (Uncertainty)
Relative estimation
The estimation is done using relative sizing by comparing one story with a sample set of previously sized stories. Relative sizing across stories tends to be much more accurate over a larger sample, than trying to estimate each individual story for the effort involved.
Teams are able to estimate much more quickly without spending too much time in nailing down the exact number of hours or days required to finish a user story.
Estimation Technique : T-Shirt Sizing
The team members are getting caught up in the idea that the number of points associated with a story has anything to do with the number of hours involved in delivering the value of that story; it may be more effective to switch to a non-numerical system like T-shirt sizing.
In this technique Items are categorized into t-shirt sizes: XS, S, M, L, XL. The sizes can, if needed, be given numerical values after the estimation is done. This is a very informal technique, and can be used quickly with a large number of items. Usually, the decisions about the size are based on open, collaborative discussion, possibly with the occasional vote to break a stalemate.
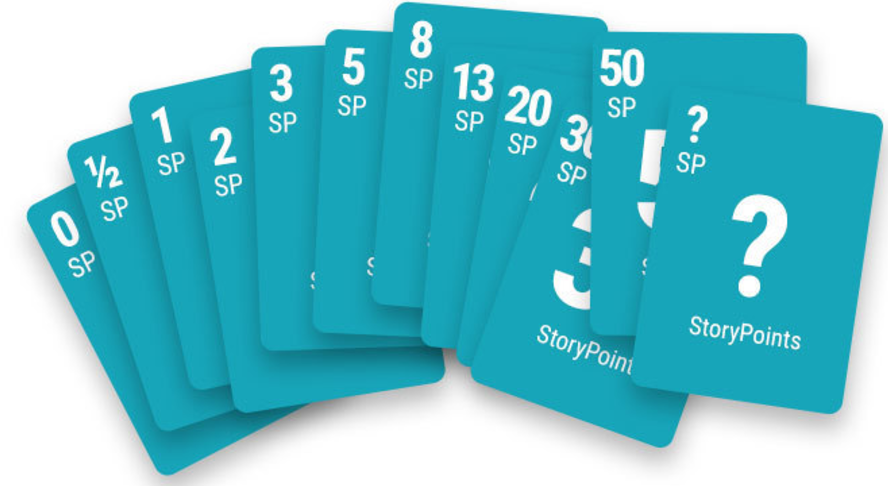
Estimation Technique : Planning Poker
Participants use specially-numbered playing cards to vote for an estimate of an item. Voting repeats with discussion until all votes are unanimous. There are lots of minor variations on Planning Poker.
The most common way is to categorize them into 1,2, 4, 8, 16 points and so on. Some teams prefer to use the Fibonacci series (1, 2, 3, 5, 8). Once the stories are ready, the team can start sizing the first card it considers to be of a “smaller” complexity.
Planning Poker Steps:
- Each estimator is given a planning poker card set, each card has valid estimate written on it.
- Product Owner reads a story and the team briefly discusses.
- Each estimator selects a card that’s his/her estimate
- Cards are turned over so all can see them.
- Discuss Differences – especially outliners.
- Re-estimate until estimates converge.
While estimating we hear the “Ideal day”/time, it’s a unit for estimating product backlog items if it were the only work being performed with no interruption and all resources.
Note:
- Product Owner doesn’t estimate.
- Scrum Master will ensure the estimation process is done properly.